Gas fees on Sui
This article focuses solely on computation fees, exploring how Sui provides stable, predictable, and low transaction fees, and why this is crucial for scalability and mass adoption.
 5 min
5 minGas fees on Sui comprise two distinct components: computation fees for transactions and storage fees for onchain storage.
This article focuses solely on computation fees, exploring how Sui provides stable, predictable, and low transaction fees, and why this is crucial for scalability and mass adoption.
How Sui gas fees are calculated
Gas price survey
At the start of every epoch (24 hours), validators are surveyed and submit the minimum price at which they are willing to process transactions. Based on these submissions, Sui determines a reference gas price, the 2/3 percentile by stake.
This setup guarantees stable gas fees for 24 hours by ensuring that at least 66% of validators agree to process transactions at the reference price, eliminating concerns about minute-to-minute fluctuations
Gas fee formula
Most transactions on Sui are executed at or near the reference price. While tipping is not necessary due to Sui’s efficient design, users still have the option to add a tip to the reference price for higher priority processing of their transactions.
Therefore, you can consider the calculation for computation gas prices as follows:
Computation Price = Reference Price + Tip
Healthy competition among validators
As validators play a crucial role in determining gas prices, there are rules that incentivize them to adhere to the reference gas price and offer cost-efficient prices.
Tallying rule
The tallying rule is a community-enforced mechanism designed to ensure validators honor the reference gas price. Throughout the epoch, validators receive signals about the behavior of their peers. These signals keep validators in check, as those who behave well receive their rewards, while bad actors face reduced / slashed rewards.
Stake incentivization
Validators receive stake rewards proportional to the amount of stake they hold. This system encourages validators to set lower gas prices to attract more users and delegators.
Lower gas fees attract more users, whose increased usage can lead to higher overall rewards. Delegators are more likely to stake their tokens with validators who are performing well. Validators offering the lowest prices are more likely to honor the reference price and receive their rewards accordingly. If validators don’t lower gas fees, they risk being priced out.
These two rules benefit Sui’s adoption as validators are encouraged to maintain a stable and cost-efficient network.
Are gas fees affected during high traffic? Sui during high traffic
While many blockchains promise stable fees in theory, they often falter during periods of high congestion. Sui stands out as an exception.
There have been three notable instances of increased traffic on Sui. During all three, Sui has maintained stable gas fees, consistently upholding its promise.
First 100 days of mainnet
Sui is designed to scale, and it demonstrated this capability within its first 100 days.
After its mainnet launch on 3 May 2023, Sui was processing around a million transactions per day.
In July 2023, Sui experienced a significant increase in traffic as many users tried out Sui 8192, a blockchain game built on the network. According to Artemis, it reached 5,414 TPS and processed over 65.8 million transactions on 27 July.
Throughout this period, gas fees remained stable and did not increase despite the surge in traffic and demand.
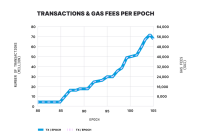
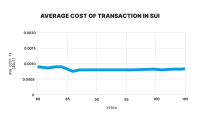
2023’s inscription craze
At the end of 2023, the blockchain space went through an inscription craze, putting many blockchains to the test.
Most blockchains saw abnormal spikes in their gas fees due to the congestion caused by inscriptions. Arbitrum even experienced an outage for almost 2 hours.
How did Sui fare?
As shown in the image below, there were two days of heightened inscription activity on Sui, during which the transactions exceeded 10 million each day. Gas fees remained stable, and the network did not experience any outages.
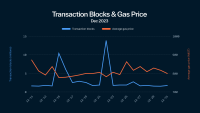
SPAM Test
SPAM, a fair distribution token, drove the recent surge in Sui’s traffic. SPAM operates on a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism where users earn tokens by sending a high volume of transactions—the more transactions sent, the greater the token reward.
Such projects effectively function as rigorous stress tests. Between 2 – 6 May, Sui consistently handled over 20 million transactions per day, all while keeping gas fees stable.
A comparable test on Solana, involving the Ore project, encountered congestion issues and dropped transactions, leading to the test being paused. In contrast, Sui’s network showcased its resilience and stability under similar pressure.
Why this matters for user adoption
Low, predictable, and stable gas fees are crucial for mass adoption.
While networks like Solana and Polygon can process many transactions with high throughput, their gas fee mechanisms are counterintuitive for businesses looking to integrate blockchains.
For instance, when ordinals launched on Polygon, transactions went from 2.9 million on 15 November to 6.1 million on 16 November. Although transactions merely doubled, this led to a 70x spike in gas fees before it settled at 4x. Businesses will be hesitant to build on blockchains if their costs can suddenly skyrocket to these multiples.
Despite its popularity, Solana is notorious for network outages. In recent months, users on X have been complaining about failed transactions due to network congestion. Businesses seeking dependable infrastructure cannot afford to rely on systems where transactions are known to fail or the network can go offline.
Users and businesses need reliable infrastructure and stable costs. Sui promises precisely that.
Stop scrolling and launch it already!
We made a web3 app that doesn’t suck. Test it out yourself now for free!

